
A well-designed perfume bottle sets the stage for a luxurious user experience. It helps to promote and represent the brand, while encouraging business growth. Tribology research addresses the problems related to the production of defective perfume bottles.
The glass forming process includes three main steps, as illustrated in Figure 1. Surface finish of the hollow glass bottle is affected by high friction and wear at the glass/tool interface. These tribological parameters are influenced by thermal dynamics, contact duration, contact pressure, tool roughness and glass viscosity. For example, low glass viscosity and a smooth tool surface will increase the contact area between the glass and tool, leading to high friction and wear ("sticking"). Tools like molds and punches are coated with lubricants (such as resins, silicone-based pastes, graphite-based oils, etc.) to reduce sticking. However, these lubricants can transfer onto the surface of the glass bottle, creating a cluster of spots (as large as 0.3 mm) that result in a defective glass bottle with poor surface finish.
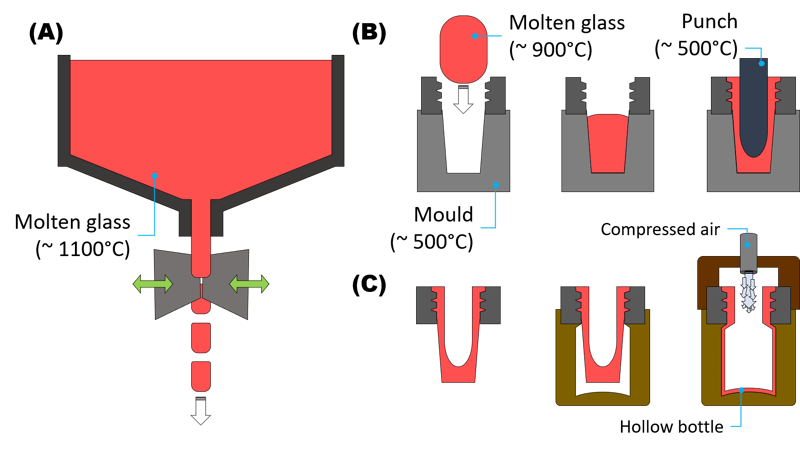 Figure 1. Glass forming process, from molten glass cutting (A), to punching (B) and blowing (C).
Figure 1. Glass forming process, from molten glass cutting (A), to punching (B) and blowing (C).
A two-step solution was implemented.
Step One: Search for a high-temperature tribometer that can simulate the thermal dynamics of glass/tool contact in a lab setting (the temperatures of glass and tools in the industrial production line are 900° C and 500° C, respectively). Ducom Multi Capability Tribometer (POD 4.0) was selected (see Figure 2). In addition to its temperature-control capabilities, it can also measure friction and wear as a function of contact pressure, speed and other material properties.
Step Two: Formulate hybrid layer coatings on the tools that can reduce interface temperature, friction and material transfer.
/Videos%20and%20Images/Applications%20and%20Blogs/POD%204.0/POD%204.1_schematic.jpg?width=669&name=POD%204.1_schematic.jpg) Figure 2. Ducom Multi Capability Tribometer (POD 4.0) with furnace heating up to 1000 °C.
Figure 2. Ducom Multi Capability Tribometer (POD 4.0) with furnace heating up to 1000 °C.
CUSTOMER BENEFIT. Using Ducom Multi Capability Tribometer (POD 4.0), several multi-layered PVD coatings were tested against the glass material. Coating AlTiCrSiN showed promising results related to friction reduction and material transfer to the glass surface. It can potentially reduce tool replacement costs and improve the surface finish of glass bottles for a variety of users, especially those in the luxury perfume industry.
These Stories on wear
USA: +1 (847) 737-1590
India: +91 (80) 4080-5555
Netherlands: +31 (85) 065 74 10